What is data encryption?
Internet nowadays is the main communication method. People do a lot of things through the internet and criminals know that. It is a new era for thieves, they don’t steal money from the banks with guns, they use data to get closer to the assets. And this is where encryption comes in.
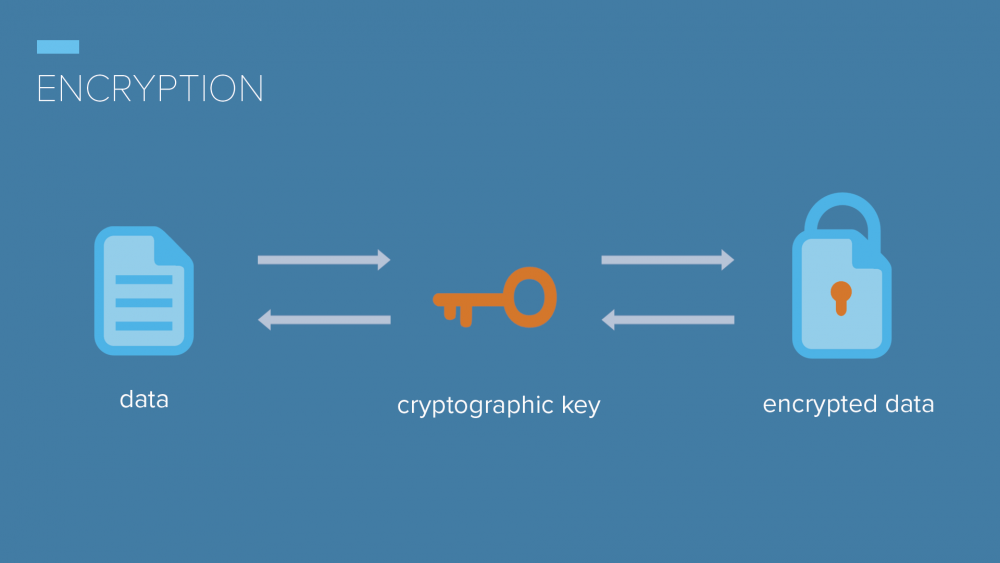
Encryption translates data into a code, that only can be read by a person who has access to a key or password. Now encryption is one of the most secure methods that organizations use. There are two types of encryption – ciphertext and unencrypted data called plaintext.
Primary function
The main function is to make sure that sensitive data is safe. The purpose is to hide important information from others by turning plaintext data into a series of random ciphertext. It would make it impossible to read plaintext without decoding the data with the decryption key.
Plaintext is a simple text that can be read by anyone, but ciphertext is unreadable by humans and computers.
Encryption keys are made to be one of a kind, by different algorithms. Key is used to decode or encode data.
Other encryption methods
If the encryption key is used to decode and encode data, that means that the key is able to mix up data into unreadable text and it works both ways.
Encrypted data can be shared if one of them has a unique key. You share your data with others and they can read your encrypted text using the key.
Encryption Algorithm
As previously said, encryption is used to protect data for e-commerce, online payments, banking, email software, cryptocurrency, and more. Encryption also protects data that is shared between two people, for example, credit card data when a person is making a purchase online. Data still can be stolen, but it would be useless for hackers and spies. Encryption isn’t just used for internet transits, but also for ATM transactions and mobile phone calls.
Basically, the encryption program runs a formula that turns readable data into unreadable data. Every encryption algorithm makes use of a key, to execute the calculations. The longer the key is, the more calculation patterns can be created. That makes it harder to decrypt the ciphertext without a key.
Most encryption algorithms use the “block cipher method”. The method applies the random algorithm in combination with a symmetric key to encrypt a block of text.
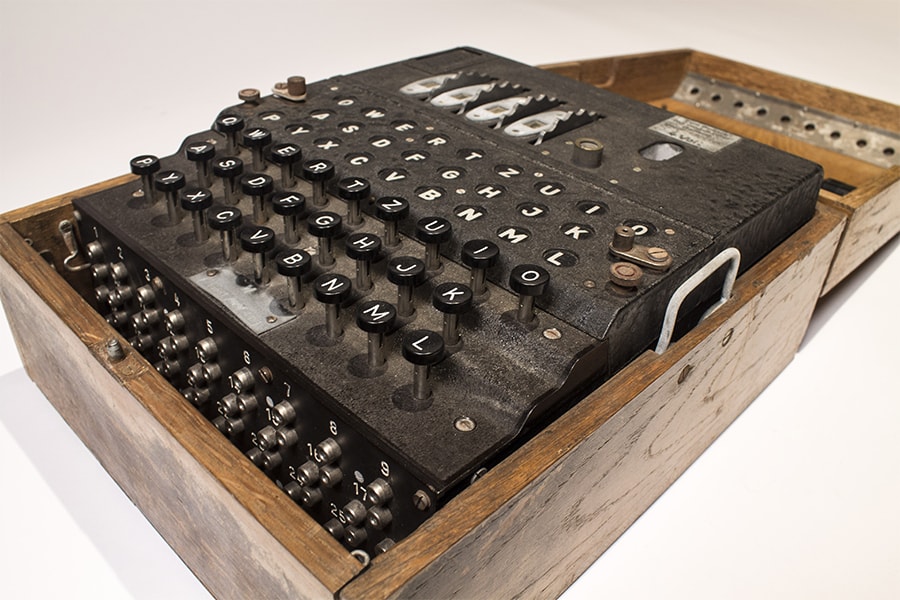

History of Encryption
First, the encrypted text was found in 1900 B.C., when Egyptians used simple encryption methods. Even Spartans used an encryption method, they wrote important messages on leather and wrapped them around a stick, but the message only could be read by a person who had the same diameter stick.
Hebrew scribes developed the encryption method as the reverse alphabet, where “A” becomes a “Z”.
The time of Julius Caesar used a method similar to the reverse alphabet. They used a pre-agreed shift of the letters. A person who knew about the pre-agreed shift of the letter could understand the message.
During WWII encryption made a big break with German cryptologists’ creation called the Enigma machine.











